How to Optimize for AI Search
The death of journalism, and tips to optimize for both GEO and SEO
Background: The Search Landscape is Changing
The way people search is shifting rapidly. According to Gartner, traditional search volume will decline by 25% by 2026. Around 60% of searches now result in no clicks at all.
We are entering the era of AI search like ChatGPT (more than 180.5 million monthly active users), Perplexity AI (search volume has jumped 858% over the past year)
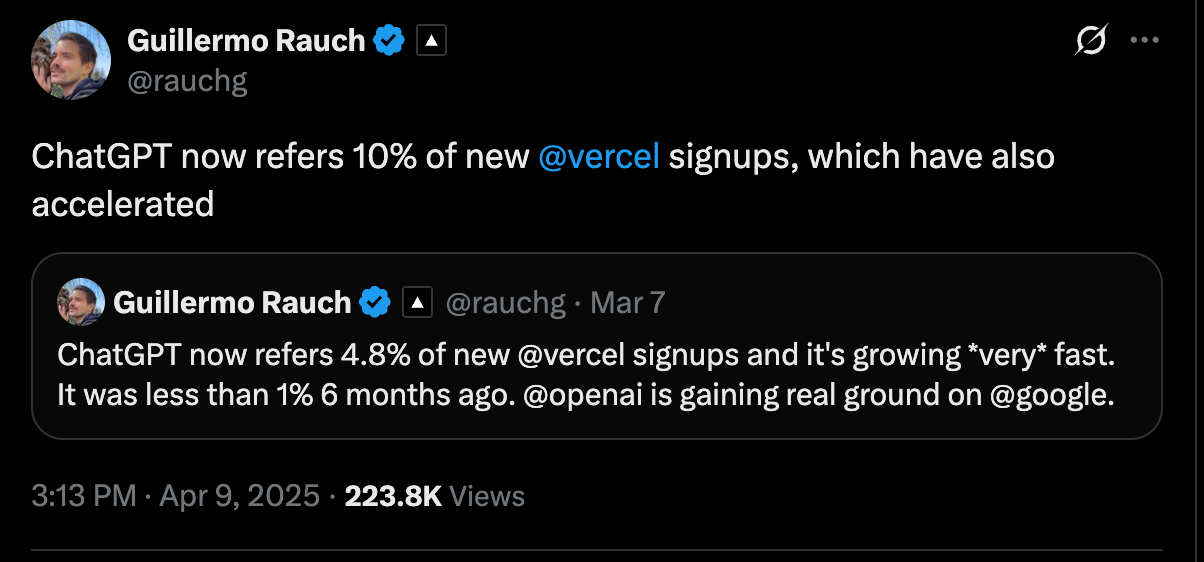
It’s not just AI search, it’s referrals from AI tools. Between September 2024 and February 2025, referral traffic from generative AI increased by 123%.
Journalist content is seeing decreasing trends. Organic traffic to The New York Times has already dropped from 44% to 36.5% in just three years. Business Insider lost 55% of Google search traffic from April 2022 to April 2025 and cut 21% of its staff last month.
“Links were the last redeeming quality of search that gave publishers traffic and revenue. Now Google just takes content by force and uses it with no return, the definition of theft.”
— Danielle Coffey, president of The News/Media Alliance
As if that weren't enough, Google’s recent rollout of AI-generated overviews above search results is accelerating this change. The “10 blue links” are no longer the crown jewel.

In SEO, you are ranked by optimizing for keywords, structure, backlinks, and user signals. In GEO, your goal is to show up in the answer itself.
Today’s search interface is powered by LLMs like GPT-4o, Gemini, and Claude. These models don’t just index—they synthesize. They remember, reason, and personalize. And that changes how you get discovered.
GEO (Generative Engine Optimization) is just built different. In this blog post, I’m thinking about how to adapt to these differences.
Three Types of AI Search Engines
LLMs
Models like GPT, Claude, Gemini, Grok, and Llama act as direct interfaces for finding information.AI Agents
Tools like Perplexity and Manas use LLMs under the hood but also add search logic, consolidate sources, generate charts, and run analysis.Hybrid Systems
Google is combining traditional indexing with generative AI. It crawls pages but now also surfaces AI summaries on top of results.
How to Optimize for AI Search
1. Add More Content Density
SEO rewarded repetition and exact keyword matches. GEO rewards clarity, organization, and depth. The goal isn’t keyword-stuffed fluff—it’s meaning-dense, structured information.
Use headings, bullet points, and summary phrases. LLMs love content they can parse easily.
SEO optimizes for keywords and metadata. GEO optimizes for conceptual clarity and contextual relevance. Because AI reads like a human (but faster), your job is to make that reading as effortless and informative as possible.
AI tools consume pages differently than bots used to. Build your content with a focus on real explanation and meaningful context.
2. Diversify Your Content Channels
AI-native search is fragmented. Different platforms—Instagram, Amazon, Siri—use different models and serve different user intents. Searches are longer (23 words vs. 4), sessions are deeper (6 minutes on average), and answers vary depending on source and context.
AI doesn’t just crawl the traditional web. It pulls from:
Reddit and forums
Wikipedia and encyclopedias
Twitter, LinkedIn, and other social networks
Expert blogs
Aggregated reviews
YouTube transcripts and other multimodal sources
The team at Ahrefs showed how AI and non-AI traffic distribute across different types of pages. Pages made just for navigation (like huge listing pages) perform poorly with LLMs.
Also, don’t ignore PDFs or non-HTML formats. LLMs don’t care—they cite those just as often.
3. Build Format for LLMs
“In 2025 the docs should be a single your_project.md file that is intended to go into the context window of an LLM.”
— Andrej Karpathy
LLMs don’t execute JavaScript. They read what’s in the HTML. So if your content only appears after JS loads, it might as well not exist.
Make your site LLM-friendly:
Add structured data (schema.org, JSON-LD)
Label entities like businesses, locations, and products clearly
Make sure core info appears without needing JavaScript
LLMs like clean, labeled, structured input. Help them help you.
4. Focus on Meaning, Context, and Intent
Traditional search tried to match exact words. LLMs try to understand the intent behind those words.
That means you’re now optimizing for the question a human meant, not just what they typed.
Write clearly. Avoid filler and fluff. Be specific. Use technical terms and real names. Answer questions directly.
For example, old SEO would optimize a page for “Best pizza NYC” by stuffing in keywords. GEO makes that page understandable as:
A review or listicle
About pizza and its ingredients, cooking time, and types
Clearly located in NYC with real addresses and businesses
It’s about helping the AI understand what your page is and what it offers—not just getting the right words on the page.
5. Correct is More than New
LLMs still consider freshness, but they’re also constantly testing for accuracy. Content that’s wrong—or just outdated—will be deprioritized.
Keep your info current. But make sure it’s right, too.
6. Focus on Mentions and Authority
Google revolutionized SEO with backlinks as a trust signal. But LLMs don’t work like that.
Instead, they infer authority from:
The context in which you're mentioned
The relevance of surrounding topics
The frequency and variety of mentions
So even unlinked mentions can matter—a lot.
For example, a site writing about pizza in NYC that casually mentions your pizzeria gives LLMs useful signals. If that context is rich and trustworthy, it boosts your brand’s association with the topic.
Links still help, especially in traditional SEO. But in GEO, entity mentions matter just as much—if not more.
7. Measure Performance with GEO Tools
Think Google lost to ChatGPT? Nope. Google search is still growing. ChatGPT’s market share is actually under 1%.
But we still need new tools to track AI-era visibility. Traditional SEO tools won’t cover it all. Try:
Traditional SEO tools – Semrush, Ahrefs, SEOmonitor, etc.
AWR – Free tool for tracking Google AI Overviews
Brand Radar – Tracks AI mentions of your brand across queries
Mangools AI Search Grader – Measures brand presence in AI-generated results
Profound – Tracks which brands appear in AI answers via thematic prompts
Also: check for traffic from domains like perplexity.ai, chat.openai.com, claude.ai, and you.com in your analytics.
8. Continue Traditional SEO Best Practices
“If you Google GEO, you’ll find agencies selling services that don’t really match query intent. LLM SEO of today is still mostly just SEO.”
— Eli Schwartz
There’s a big overlap. Fast sites, crawlable content, helpful articles, internal linking—it all still matters.
The key difference is in intent and interface. Instead of ranking in the top 10 links, you're trying to be the answer.
Think in terms of topic clusters and content hubs. Use internal linking to strengthen those connections.
If you have a page about NYC pizza styles, link to your page on “Top 10 pizza places in NYC.” Think in entities and relationships, not just pages and keywords.
How to Think About The Shift from GEO to SEO
Traditional search was built on links. GEO—Generative Engine Optimization—is built on language.
Think about how LLMs were trained and on what data
Think about how they process context and meaning, not just text
Think about how the search workflow looks now, for a user and for an AI system
The core idea is still the same: be helpful, be findable, be trusted. Just build it for a different reader now—one with a bigger context window and a better memory.
I have seen a lot of complaints from content creators on the new AI-powered search model that doesn’t give creators and journals enough credit. On the other hand, the reason SEO spam exists is that’s what the web’s search-driven business model rewards. If an AI-driven model rewards original thinking and deep knowledge, we may be on the edge of a golden era for real content again.